Diagnosis and treatment
Do I need hip surgery?
The hip is a ball and socket joint. The ball part of the joint is called the head of the femur (the thigh bone) and the socket is called the acetabulum, which is part of the pelvis.
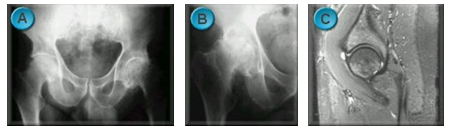
When your hip is arthritic and painful the options for treatment are limited (image A). Painkillers and anti-inflammatories can help temporarily but often the side effects are unpleasant. Sometimes an injection of local anaesthetic and steroid is used to relieve severe symptoms for a few months. With time the hip may stiffen and become less painful, but it may collapse causing the leg to shorten, making surgery more complex (image B).
Certain conditions may be amenable to keyhole surgery, usually after an MRI scan has been performed (image C). If the pain is getting worse and is affecting your mobility, then you might wish to consider having a hip replacement or resurfacing.
Total hip replacement (THR)
Thousands of total hip replacements are performed every year, and the results are usually excellent.
The components are usually made of materials such as stainless steel, titanium and polyethylene. In some cases ceramic and metal bearings are used. Pain can be dramatically reduced, and most patients are independently mobile within a few weeks of surgery.
The vast majority of people who have had a hip replacement return to all of their normal activities within a few months of surgery. Total hip replacements can be performed in young patients who have had problems such as hip dysplasia, and leg length can be restored.
Hip resurfacing
Total hip replacements in young patients are effective for a few years but then they wear out, particularly if you're working or play sports. When a hip replacement wears out it is likely that the operation will have to be repeated (revision surgery), which can be complicated.
Hip resurfacing was developed to overcome some of these problems. The resurfacing is made of a durable metal alloy (chrome cobalt molybdenum) which wears very slowly. Because of this, the bearing can be made large enough to fit over the head of the femur which is removed when a conventional hip replacement is used. If the hip resurfacing fails at a later date, revision surgery is much more straightforward compared with a conventional hip replacement.
Hip resurfacing is a relatively new technique, which was developed to treat painful arthritis in younger more active patients. The results are usually excellent, and in many ways better than the results of hip replacement. The risk of dislocation, one of the commonest complications of hip replacement, is virtually eliminated with hip resurfacing. Most patients who have had hip resurfacing return to work and sports within a few months of surgery.
Hip resurfacing is still regarded as an experimental operation because it has not been performed for as long as hip replacement. The results in the short to medium term are excellent, but we do not yet know what the long-term (10+ years) results are. Some people are concerned about the effects of long-term exposure to chromium and cobalt. High concentrations of these metals can damage cells or cause allergic reactions, but there is no convincing evidence available to show that these bearings will harm your health.
Revision hip surgery
Hip replacements are mechanical bearings that will eventually wear out. If you have a hip replacement when you are young, it is more than likely that it will wear out within your lifetime. When a hip replacement wears out, it usually becomes loose and painful. If this happens, the components of the hip replacement need to be removed and new ones inserted. This procedure is called revision hip surgery. It is often quite a complex operation because the components have to be removed without damaging the remaining bone, and the surgeon has to ensure that the new components are solidly fixed into place. Compared to having a hip replacement for the first time, the risk of complications is higher and it often takes longer to recover.
If your hip replacement is painful, or it doesn't feel 'right' please contact us. A clinical assessment and appropriate x-rays will usually tell us if there is a problem. If you need to have revision hip surgery it is usually better to have it done sooner rather than later, to reduce the risk of further complications.
Hip arthroscopy
A relatively small number of conditions may be suitable for keyhole surgery. These include problems with the labrum or sealing ring around the socket and loose bodies within the joint. Unlike knee arthroscopy, patients usually need to stay in hospital for one or two days afterwards.